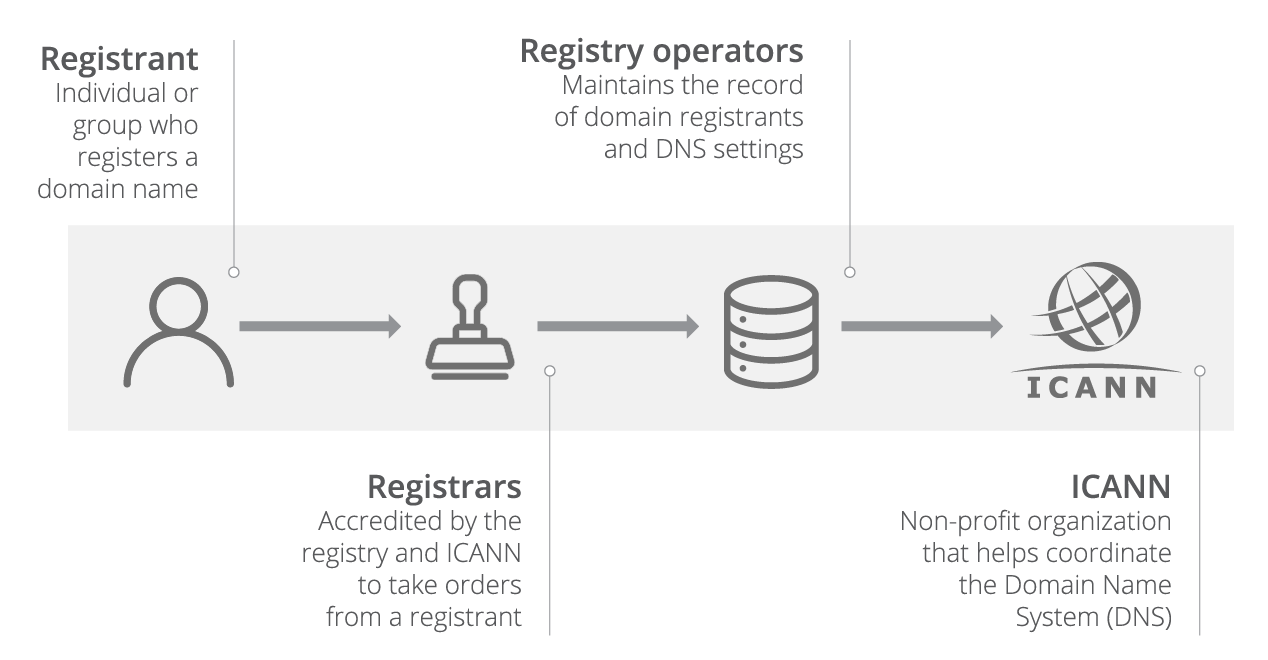
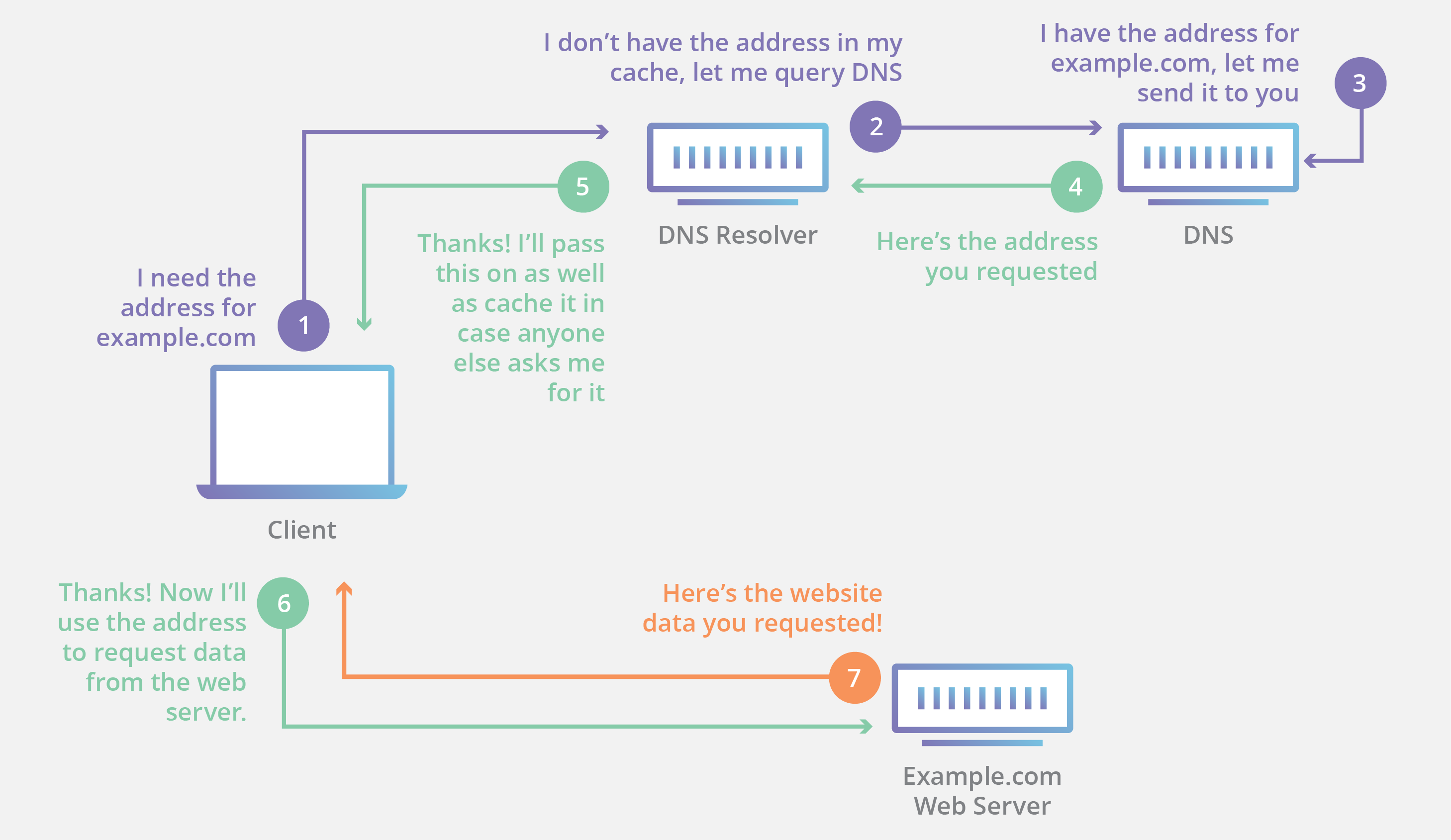
20 What S A Domain Name Definition New

Domain names provide an easy way to remember internet address which is translated into its numeric address ip address by the domain name system dns.
What s a domain name definition. In the same way that a gps needs a street address or a zipcode to provide directions a web browser needs a domain name to direct you to a website. Updated on november 27 2019 in simple terms a domain name system dns is a collection of databases that translate hostnames to ip addresses. Domain names are used to identify one or more ip addresses.
In this tutorial we will learn domain meaning and types with the purpose and difference with the domain and hosting. Short for domain name system dns is an internet service that translates domain names to ip addresses domain names are alphabetic and therefore easy to remember but the internet is based on numeric ip addresses so a dns server is required for computers to communicate with one another. Domain names are used in urls to identify particular web pages.
The domain name is mapped to an ip address which represents a physical point on the internet. More than one domain name can be mapped to the same internet address. This allows multiple individuals businesses and organizations to have separate internet identities while sharing the same internet server.
Users generally do not know or misinterpret the domain keyword meaning. A domain name is used for finding and identifying computers on the internet. In a lot of ways a domain name has the same relationship to a website as a street address has to a house.
However it is difficult for humans to remember strings of numbers. A domain name is an identification string that defines a realm of administrative autonomy authority or control within the internet. The domain can be used in different areas of computer science.
A domain name is a unique set of characters that identifies a specific website. A domain name is essentially your website s equivalent of a physical address. Domain names are used in various networking contexts and for application specific naming and addressing purposes.